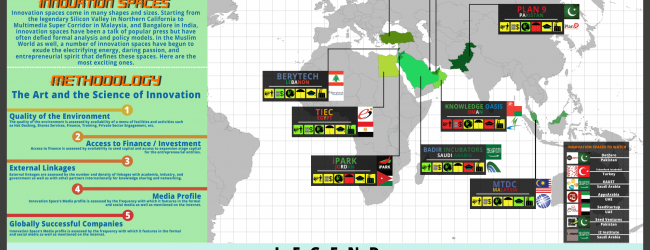
Innovation spaces come in many shapes and sizes. Starting from the legendary Silicon Valley in Northern California, to Route 128 in Boston, Research Triangle Park in North Carolina, Multimedia Super Corridor in Malaysia, and Bangalore in India, innovation spaces have been a talk of popular business and technology press, but have often defied formal analysis and policy models. Part of the lure of the Silicon Valley, is in its culture, its willingness to accept failure, and the eagerness of its investors to take a chance. At a smaller scale too, innovation spaces are often defined by the electrifying energy, that is often ‘in the air.’
In the Muslim World, like in the rest of the world, the last decade or so has seen the emergence of innovation spaces, that have begun to exude this electrifying energy, this daring passion, and the entrepreneurial spirit critical to success. Here is a list of the most exciting ones among them…
Methodology: The Art and the Science of Innovation
1. Quality of the Environment
The quality of the environment is measured by availability of a menu of facilities and activities such as Hot Desking, Shares Services, Finance, Training, Private Sector Engagement, etc.
2. Access to Finance / Investment
Access to finance is measured by availability to seed capital and access to expansion stage capital for the entrepreneurial entities.
3. External Linkages
External linkages are measured by the number and density of linkages with academia, industry, and government, as well as with other partners internationally, for knowledge sharing and networking.
4. Media Profile
Innovation Space’s Media profile, is measured by the frequency with which it features in the formal and social media, as well as mentioned on the internet.
5. Globally Successful Companies
Globally successful companies are measured by number of companies, that have ventured abroad and made a name in the global markets and the size of their success.
SPACE, EQUIPMENT, SERVICES
TRAINING PROVIDED
FUNDING PROVIDED
OWNERSHIP
ACADEMIC LINKAGES
ENTREPRENEURIAL & INDUSTRIAL LINKAGES
You must be logged in to post a comment.